Why Choose Lowfat Milk for Your Health and Nutrition Needs
Lowfat milk has emerged as a popular choice for health-conscious individuals seeking to balance nutrition and flavor. As consumers become more aware of dietary needs, the shift towards lower-fat dairy options is significant. Nutrition expert Dr. Emily Carson, a registered dietitian, emphasizes this trend by stating, “Lowfat milk offers essential nutrients without the extra calories, making it an excellent option for those looking to maintain a healthy weight.” This powerful perspective highlights the importance of lowfat milk in a balanced diet.
Incorporating lowfat milk into daily nutrition not only helps in managing calorie intake but also provides essential vitamins and minerals, such as calcium and vitamin D. With the growing prevalence of obesity and related health issues, choosing lowfat milk can be a straightforward yet effective strategy to promote overall well-being. The nutritional benefits, paired with its versatility in cooking and baking, make lowfat milk an invaluable component of a healthy diet.
Moreover, as research continues to support the health benefits of lowfat dairy products, it is clear that this choice aligns well with contemporary dietary recommendations. By understanding the advantages of lowfat milk, individuals can make informed decisions that enhance their health and nutrition, paving the way for a healthier lifestyle.

Benefits of Lowfat Milk in Supporting Weight Management and Health Goals
Low-fat milk is an invaluable resource for those aiming to manage their weight while still enjoying the nutritional benefits of dairy. According to the 2020-2025 Dietary Guidelines for Americans, low-fat dairy products can help individuals meet their recommended daily intake of calcium and vitamin D, essential nutrients crucial for bone health. Replacing whole milk with low-fat options can lead to significant reductions in calorie intake; research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition indicates that substituting full-fat dairy with low-fat alternatives can decrease daily caloric consumption by approximately 100 calories, which can contribute effectively to weight management goals.
In addition to aiding in weight control, low-fat milk provides ample protein—about 8 grams per cup—which is vital for muscle repair and growth. A study reported in the Journal of Nutrition highlights that protein-rich diets, combined with low-fat dairy, may promote a feeling of fullness, potentially preventing overeating. Furthermore, incorporating low-fat milk into a balanced diet has been associated with a lower risk of developing obesity-related conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease, as supported by findings from the National Institutes of Health. These benefits underscore the relevance of low-fat milk in a health-conscious diet, aligning with individuals' nutritional goals while maintaining a delicious taste.
Nutritional Comparison: Lowfat Milk vs. Whole Milk in Daily Diet
When comparing lowfat milk to whole milk, the nutritional differences can significantly impact daily dietary choices. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, 1 cup of lowfat milk (1% fat) contains about 102 calories and 2.5 grams of fat, while whole milk (3.25% fat) packs around 150 calories and 8 grams of fat. This reduction in fat and calories in lowfat milk can be particularly beneficial for those monitoring their weight or dietary fat intake. Moreover, lowfat milk retains similar levels of protein and essential vitamins, including calcium and vitamin D, which are crucial for bone health and metabolic function.
In addition, a study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition highlights that replacing whole milk with lowfat alternatives can lower the risk of cardiovascular disease. The research indicates that a diet lower in saturated fats, commonly found in whole milk, can improve cholesterol levels and decrease heart disease risk. With lowfat milk offering comparable nutrient density without the excess calories and fats, it serves as a smart choice for individuals seeking a balanced diet while maintaining their health and nutrition needs.
Why Choose Lowfat Milk for Your Health and Nutrition Needs
This chart compares the nutritional content of lowfat milk and whole milk, highlighting the differences in calories, fat, and calcium content, which can influence your daily diet choices.
Impact of Lowfat Milk on Cardiovascular Health: Key Studies and Findings
Research has shown that lowfat milk can play a significant role in promoting cardiovascular health. A meta-analysis published in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition revealed that individuals who consume lowfat dairy products have a lower risk of developing cardiovascular diseases compared to those who consume high-fat dairy options. The study highlighted that substituting high-fat dairy with lowfat versions can lead to a reduction in overall saturated fat intake, which is crucial for maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
Moreover, a survey conducted by the American Heart Association found that incorporating lowfat milk into a balanced diet can be beneficial for blood pressure regulation. Participants who included lowfat dairy in their diet exhibited improved blood pressure readings compared to those who did not, suggesting that lowfat milk might serve as a heart-healthy alternative. Furthermore, the calcium and potassium content in lowfat milk is associated with better vascular function, which can be instrumental in reducing hypertension and promoting overall heart health. These findings underscore the importance of choosing lowfat milk as part of a nutritional strategy aimed at enhancing cardiovascular wellness.
Lowfat Milk's Role in Calcium Intake and Bone Health Maintenance
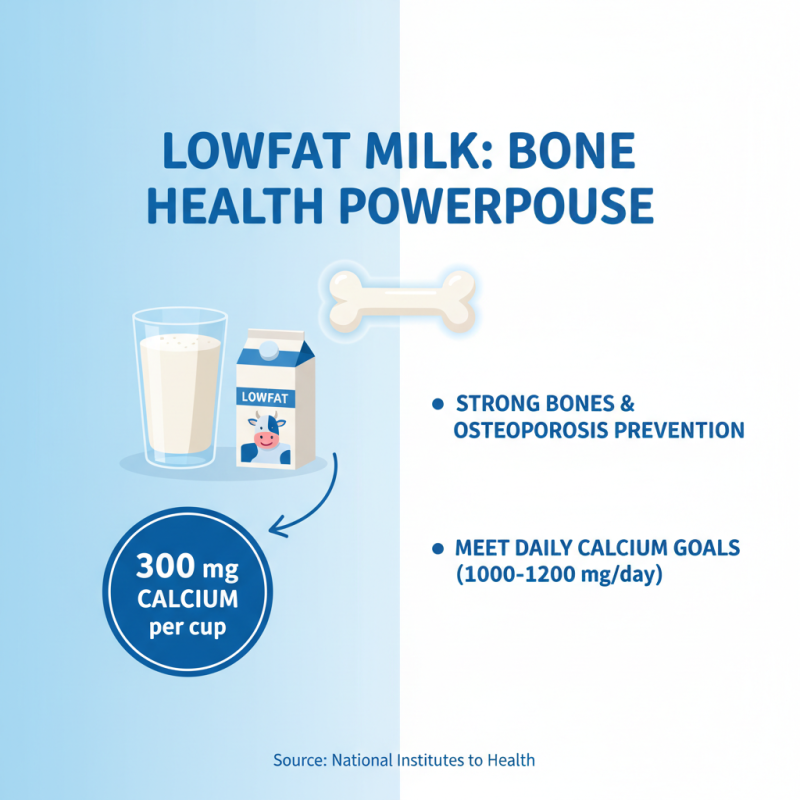
Lowfat milk is an excellent source of calcium, a vital nutrient for maintaining strong bones and overall bone health. According to the National Institutes of Health, adults should aim for 1,000 to 1,200 mg of calcium daily, and lowfat milk can contribute significantly to this requirement. One cup of lowfat milk provides approximately 300 mg of calcium, making it one of the most accessible dietary sources. Regular intake of calcium-rich foods like lowfat milk can help prevent osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones, especially in older adults.
Incorporating lowfat milk into your diet can be simple and delicious. Add it to smoothies, warm it up in soups, or enjoy it with whole-grain cereals. If you are lactose intolerant, consider lactose-free lowfat milk options that still provide the same calcium benefits without the discomfort.
**Tips**:
- Make it a habit to consume lowfat milk daily to meet your calcium needs effectively.
- Pair lowfat milk with vitamin D-rich foods or supplements, as vitamin D enhances calcium absorption, promoting better bone health.
- Experiment with lowfat milk in various recipes to discover new ways to integrate it into your meals, helping you maintain an enjoyable and nutritious diet.
Understanding Lactose Intolerance: Lowfat Milk as a Suitable Alternative
Lactose intolerance affects approximately 68% of the global population, particularly among certain ethnic groups. This condition occurs when the body lacks the enzyme lactase, making it difficult to digest lactose, the sugar found in milk and dairy products. For individuals experiencing discomfort from lactose consumption, lowfat milk presents a practical alternative that retains a host of nutritional benefits while minimizing lactose levels. Research indicates that many people with lactose intolerance can tolerate lowfat milk, which typically contains about 5 grams of lactose per cup—significantly less than whole milk.
Choosing lowfat milk not only provides essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D but also offers a reduced fat option that can support heart health. According to the National Dairy Council, lowfat milk supplies about 8 grams of protein per serving, making it a great option for muscle maintenance and overall health. Moreover, it provides a creamy texture and flavor that can enhance various dishes without adding excessive calories or fat.
Tips: If you're transitioning to lowfat milk from whole milk, consider incorporating it gradually into your diet to allow your digestive system to adjust. For those who are highly sensitive, lactose-free lowfat milk is an excellent choice, as it undergoes processing to break down lactose while retaining all other nutrients. Experiment with lowfat milk in smoothies or baked goods to enjoy its benefits without discomfort.
Related Posts
-

2025 Top 10 Nutrition Facts You Didn’t Know About Skim Milk
-

10 Essential Tips for Using a Whipped Cream Can Like a Pro
-

Top Benefits of Fat Free Milk: A Healthy Choice for Weight Loss and Nutrition
-

How to Get Essential Nutrition from Skim Milk: Benefits and Tips
-

What is Heavy Whipping Cream and How to Use It in Your Recipes
-

Top Benefits of Low Fat Milk Nutrition for a Healthier Lifestyle