How to Understand Low Fat Milk Nutrition for a Healthier Lifestyle
Understanding the nutritional aspects of low fat milk is essential for those striving for a healthier lifestyle. According to Dr. Emily Johnson, a renowned nutritionist and expert in dairy products, "Low fat milk nutrition plays a pivotal role in achieving a balanced diet, providing essential nutrients without the extra calories." This insight reflects the growing interest in how low fat milk can serve as a nutritious alternative for individuals looking to reduce their fat intake while still benefiting from the vital nutrients that dairy products offer.
Incorporating low fat milk into your diet can lead to numerous health benefits, including improved heart health, weight management, and enhanced bone strength. Low fat milk retains the protein, calcium, and vitamins found in whole milk while cutting down on saturated fat, making it an optimal choice for those concerned about caloric intake. By understanding low fat milk nutrition, consumers can make informed decisions about their dairy consumption, ensuring they meet their dietary goals without compromising on taste or nutrition. As we delve deeper into the world of low fat milk, we will explore its benefits, nutritional content, and tips for integrating it into a balanced diet.

Understanding the Nutritional Profile of Low Fat Milk
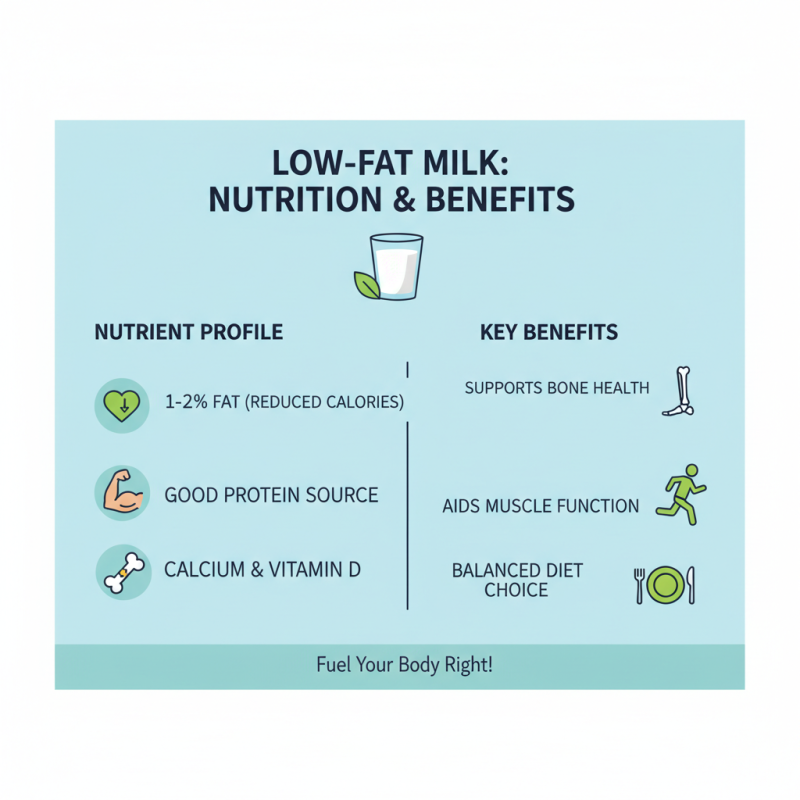
Low fat milk is a popular choice for those looking to maintain a balanced diet while still enjoying the nutritional benefits of dairy. The nutritional profile of low fat milk reveals that it retains many essential nutrients found in whole milk, but with reduced fat content. Typically, low fat milk contains about 1% to 2% fat, which significantly lowers the calorie count while providing a good source of protein, calcium, and vitamin D. These nutrients play crucial roles in bone health, muscle function, and the overall maintenance of bodily functions, making low fat milk a suitable option for health-conscious individuals.
One of the key advantages of low fat milk is its ability to offer the same creamy texture and taste as whole milk, without the added calories from higher fat content. For those looking to reduce their saturated fat intake, low fat milk serves as a guilt-free alternative that can seamlessly fit into various diets. Additionally, low fat milk is rich in B vitamins, particularly riboflavin and vitamin B12, which are important for energy production and maintaining nerve health. Incorporating low fat milk into daily meals and snacks can help individuals meet their dietary requirements, ultimately fostering a healthier lifestyle.
Health Benefits of Low Fat Milk Compared to Whole Milk

Low fat milk has been gaining popularity as a healthier alternative to whole milk, primarily due to its reduced calorie and fat content. According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, low fat milk contains about 1% to 2% fat, compared to whole milk, which typically has around 3.25% fat. This reduction in fat leads to a significant decrease in calorie consumption—one cup of low fat milk provides approximately 100 calories, while a cup of whole milk can offer around 150 calories. This calorie difference can support weight management efforts when included in a balanced diet.
In addition to lower calories, low fat milk retains essential nutrients that contribute to overall health. It is a rich source of calcium, vitamin D, and protein, all of which are critical for maintaining bone health and muscle function. Research published in the Journal of Nutrition indicates that individuals who consume low fat dairy products are more likely to meet their daily calcium requirements and have a lower risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. Moreover, the American Heart Association notes that the saturated fat found in whole milk may raise LDL cholesterol levels, thus increasing the risk of heart disease. By opting for low fat milk, one can still enjoy the nutritional benefits of dairy without the added risk associated with higher fat content.
Key Vitamins and Minerals Found in Low Fat Milk
Low fat milk is not only a popular dairy choice for those seeking a healthier lifestyle but also a rich source of essential vitamins and minerals. One of the key nutrients found in low fat milk is calcium, which is crucial for maintaining strong bones and teeth. According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, adults should aim for 1,000 mg of calcium per day, and a single cup of low fat milk can provide about 30% of this requirement. Additionally, low fat milk is fortified with vitamin D, which aids in calcium absorption and supports immune function. Studies suggest that sufficient vitamin D levels can reduce the risk of osteoporosis, especially in older adults.
Another significant component of low fat milk is vitamin B12, important for nerve function and the production of DNA and red blood cells. The National Institutes of Health recommends a daily intake of 2.4 mcg of vitamin B12 for adults, and low fat milk contributes approximately 18% of this value per serving. Furthermore, low fat milk contains riboflavin (vitamin B2), which helps in the energy production process by breaking down fats, carbohydrates, and proteins. Overall, incorporating low fat milk into your diet can be an effective way to enhance nutritional intake, supporting a balanced lifestyle while still enjoying a variety of beverages.
Recommended Daily Intake of Low Fat Milk for Optimal Health
Understanding the recommended daily intake of low-fat milk is crucial for individuals seeking to improve their overall health. Various health organizations suggest that adults consume about 2 to 3 servings of dairy per day, which can be effectively met through low-fat milk options. According to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, low-fat and fat-free dairy products are excellent sources of essential nutrients such as calcium, potassium, and vitamin D, all of which are vital for maintaining bone health and proper functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Research published in nutrition journals indicates that incorporating low-fat milk into one's diet can significantly contribute to meeting daily nutrient requirements with fewer calories and less saturated fat compared to whole milk. For instance, a serving of low-fat milk provides approximately 150 calories and 8 grams of protein, making it an efficient option for those aiming to manage their weight while still obtaining necessary nutrients. Furthermore, studies suggest that a diet rich in low-fat dairy products is associated with a lower risk of hypertension and may even help in weight management. Hence, aiming for 2 to 3 servings of low-fat milk daily can support a balanced diet, promote bone health, and enhance overall well-being.
Myths and Facts About Low Fat Milk and Weight Management
When it comes to low fat milk, misconceptions abound, particularly regarding its impact on weight management. One prevalent myth is that low fat milk can aid in weight loss, suggesting that choosing it over whole milk will significantly cut calorie intake. While substituting low fat milk for whole milk can reduce fat consumption, it is essential to remember that overall calorie balance, not just fat content, plays a critical role in weight management. Simply replacing whole milk with low fat options does not guarantee weight loss; instead, it calls for a broader perspective on dietary habits and lifestyle choices.
Another common belief is that low fat milk lacks essential nutrients compared to its full-fat counterpart. This is a misconception, as low fat milk retains most of the vital vitamins and minerals, such as calcium and vitamin D, necessary for maintaining bone health and overall wellbeing. While the fat content is reduced, the other nutritional benefits remain intact. Emphasizing low fat milk in a balanced diet can support a healthier lifestyle without sacrificing nutrient intake. Understanding these facts helps individuals make informed choices about including low fat milk as part of their dietary regimen while effectively managing their weight.
How to Understand Low Fat Milk Nutrition for a Healthier Lifestyle
| Nutritional Component | Low Fat Milk (1 cup) | Whole Milk (1 cup) | Skim Milk (1 cup) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 102 | 150 | 83 |
| Total Fat | 2.4 g | 8 g | 0.2 g |
| Saturated Fat | 1.5 g | 5 g | 0 g |
| Protein | 8 g | 8 g | 8 g |
| Calcium | 305 mg | 276 mg | 302 mg |
| Vitamin D | 120 IU | 120 IU | 120 IU |
Related Posts
-

Top Benefits of Low Fat Milk Nutrition for a Healthier Lifestyle
-

How to Get Essential Nutrition from Skim Milk: Benefits and Tips
-

How to Choose the Best Low-Fat Milk for Your Health and Diet
-

What is Heavy Whipping Cream and How to Use It in Your Recipes
-

What is Lactaid Milk? Benefits, Uses, and Key FAQs Uncovered
-

What are the Ingredients in Lactose Free Milk and How is it Made